TL; DR:
- AI transforms risk management by providing real-time insights from vast data sets, allowing financial institutions to assess risks more quickly and accurately.
- AI-powered fraud detection systems analyze customer behavior, identify irregularities, and reduce false positives.
- Financial processes such as loan approvals and investment management can be automated using AI. It enable faster, data-driven decisions with minimal human intervention, improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency in financial services.
- AI-driven Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) interprets both structured and unstructured data, significantly improving efficiency in processes like loan origination and KYC.
- AI helps financial institutions comply with current AML and KYC regulations by automating audits and reporting.
AI is driving a seismic shift in finance, with over $35 billion invested in 2023 alone and global investments projected to grow to $97 billion by 2027. It is clear that interest in AI is growing at an unprecedented scale. AI has diverse use cases for industries, including the finance sector.
Let’s explore the applications of ai in finance and its benefits
1. Risk Management
Risk assessment used to be a long, manual process. Teams would spend months mapping out risks, rating them, and finding control measures as part of the Risk and Control Self-Assessment (RCSA). On top of that, risk managers worked in silos, which didn’t help with finding more significant issues.
Without measurable data from other departments that supported risk ratings, any data collected had control gaps and faced delayed attention.
But with AI solutions, banks now have real-time insights into risks, taken from large data sets. So, instead of working with snapshots of outdated data, AI allows them to analyze a ton of variables at the same time—such as credit scores, transaction histories, and market trends. This shift helps banks and financial institutions react immediately and stay ahead of threats.
AI tools can also assess risks early in the customer onboarding phase, from verifying a customer's identity to analyzing transaction patterns. For example, Arya AI’s KYC Extraction and CKYC retrieve customer data quickly, lowering onboarding risks.
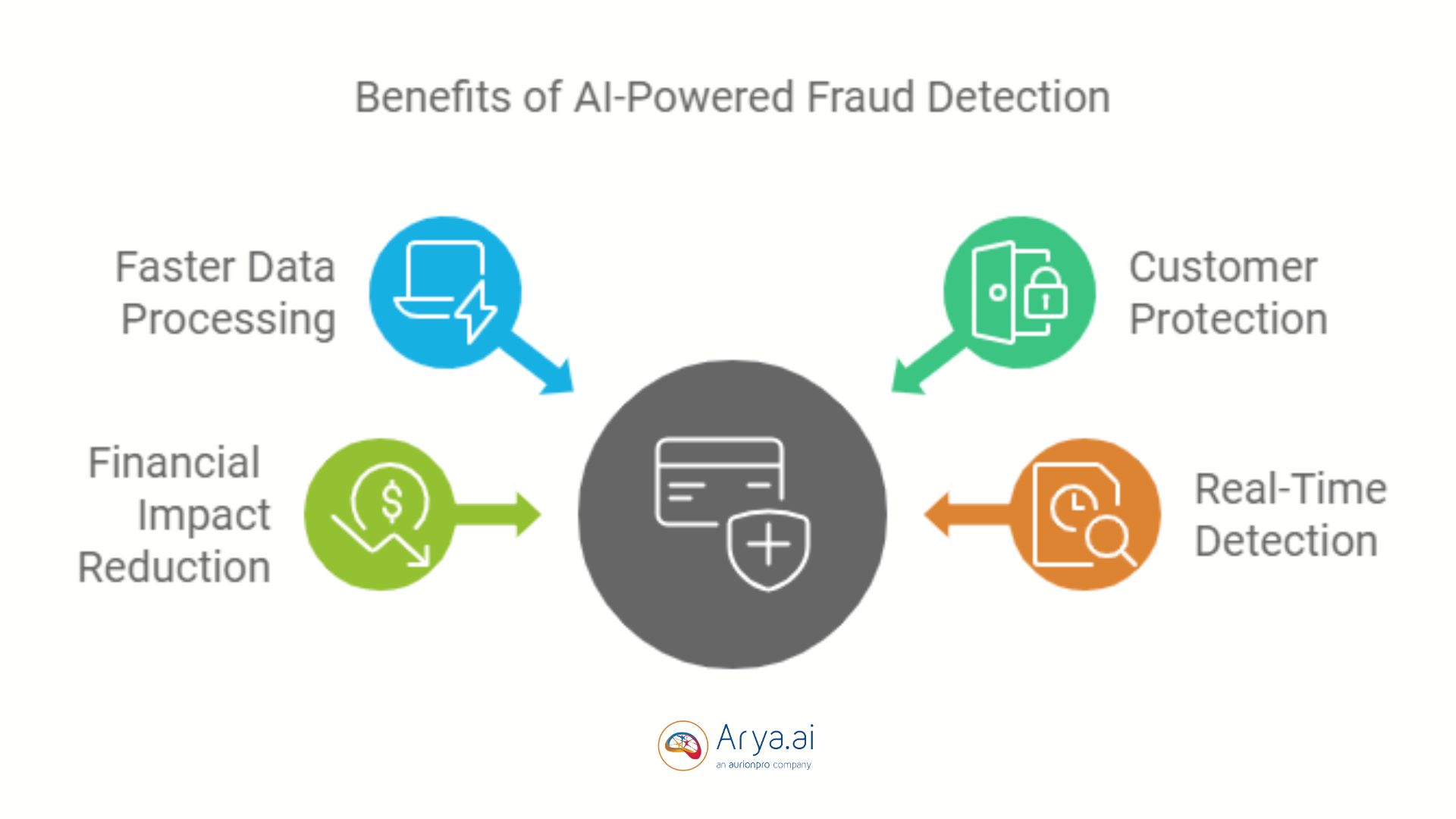
2. Fraud Detection & Mitigation with AI
Predefined rules, such as transaction limits or flagged locations, do not work on fraudsters anymore who strive to figure out how to get around these basic protections. Automated transaction monitoring systems can flag anomalies that break normal transaction patterns, which could be a sign of money laundering or fraud.
Behavioral analysis refines these processes better by creating profiles for each customer that change with every interaction. Supervised learning (with data that has been previously labeled) and unsupervised models (which identify irregularities in data without labels) both detect a range of fraud activities, from payment fraud to identity theft.
AI automates aspects of Customer Due Diligence (CDD), like identity verification and risk assessment, in AML and KYC. Natural language processing (NLP) also helps analyze written or spoken communications to to spot signals of potential scams during live interactions.
As phishing, AI-Generated Fake IDs, and money laundering grow complex, AI systems continue learning from emerging data patterns. The result is a comprehensive fraud detection framework that minimizes false positives while enhancing security.
3. Autonomous Decision-Making in Finance
Autonomous finance refers to financial systems that can operate with little to no human intervention. By using AI, these systems can automate tasks like investment strategies, loan approvals, and portfolio management, making processes faster and more efficient.
Robo-advisors such as Wealthfront and Betterment handle investments without needing human input by using algorithms to distribute funds according to a user's risk level and financial objectives. In the same way, blockchain smart contracts can automatically enforce agreements, ensuring compliance without the need for middlemen.
Switching from manual to autonomous decision-making offers advantages like increased speed, precision, and the ability to handle more tasks in financial processes.
AI’s Role in Reducing Human Intervention in Financial Decisions
AI-powered financial systems reduce the need for human input, especially in tasks that are repetitive and need a lot of data. AI tools in credit scoring and insurance underwriting provide unbiased insights by looking at data objectively.
Automated credit scoring systems analyze large datasets quickly, leading to more precise loan approvals. AI-based investment management applications adjust portfolios in real time, reducing the risk of human error during volatile market conditions.
With fewer manual processes, institutions can also reduce operational costs.
4. Document Intelligence in Finance
While OCR only captures structured data, Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) uses NLP, deep learning, and computer vision to interpret structured, semi-structured, and unstructured documents. Such systems understand content in context, extract relevant information, and integrate it into workflows.
IDP greatly enhances efficiency in areas like loan processing, compliance verification, and KYC procedures by reducing manual work and errors. JP Morgan, for example, reported reducing manual work by almost 90% with AI-based cash flow software.
Additionally, AI improves document retrieval accuracy, allowing employees to locate relevant information quickly in large document repositories, such as during mortgage origination or tax audits.
5. Compliance with Regulations (Existing & Upcoming)
Compliance with AML policies, KYC mandates, and transaction monitoring is resource-intensive. However, AI-driven tools can automate reporting and audits while keeping real-time transaction monitoring.
Deep learning-based AML systems can adapt to can adapt to new patterns of fraud. As regulators now encourage the use of AI in reporting and risk management processes, banks and financial firms worldwide are adopting RegTech (Regulatory Technology) platforms to meet compliance requirements.
At this stage, regulatory bodies are also shifting their focus to the governance of AI usage, leading to the emergence of AI-specific laws.
Preparing for Upcoming AI-Related Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies are actively working on AI-specific rules to address potential risks like AI-led fraud and deepfakes. The European Union’s AI Act aims to regulate high-risk AI systems, including those used in fraud detection and other financial applications.
New regulations are also focusing on deepfake laws, where AI-generated impersonations can disrupt operations or enable fraud. As financial firms brace for these challenges, understanding both compliance laws and technology trends will be crucial.
Conclusion
AI is transforming finance by driving efficiency, improving decision-making, and reducing risks. It is helping financial institutions detect fraud, automate operations, and comply with evolving regulations. The shift towards autonomous systems saves time and improves accuracy across processes.
As AI technologies grow, financial institutions must keep up with advancements and adapt to new regulatory frameworks. Solutions like those from Arya AI show the potential of AI to streamline operations while securing transactions and protecting customers. The future of finance lies in using AI’s capabilities to stay competitive and deliver faster, more secure financial services.