As the world went digital, financial institutions constantly struggled to balance security with a seamless customer experience. Since 2004, the RBI made it mandatory for all Indian financial institutions to verify the identity and address of all customers. Know Your Customer (KYC) procedure then became the exclusive form of verification.
The catch, however, was that every time an individual wanted to open a bank account or an investment portfolio, they had to repeat the KYC verification. While being frustrating and time-consuming for customers, this also hogged up a lot of resources for financial institutions.
To put an end to this, the Indian government launched the revolutionary Central KYC (CKYC) in July 2016. With a centralized repository of customer KYC information, CKYC eliminates the need for repeated document collection and verification. This translates to faster customer onboarding, reduced operational costs, and a more efficient KYC management system for your business.
The following is a complete guide on CKYC, and how financial institutions can leverage it. We'll explore how CKYC works, its benefits, and the steps involved in integrating CKYC into existing workflows. We'll also address potential challenges and how AI can address and accelerate CKYC processes.
What is CKYC?
Central Know Your Customer (CKYC) is a system implemented by the Indian Ministry of Finance to streamline KYC verification procedures for financial institutions. It establishes a centralized repository managed by the Central Registry of Securitization Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest of India (CERSAI). This database houses the KYC information of individuals who have undergone the CKYC process.
Think of CKYC as a secure digital vault that stores the KYC details of a person after they complete the process with a participating financial institution. This eliminates the need to go through the entire KYC hassle again when dealing with other institutions.
Here's the key takeaway: CKYC assigns a unique identification number to a customer that acts as their KYC passport across various financial service providers in India. No more piles of paperwork or repeated verifications – just a smooth and efficient onboarding experience.
How Does CKYC Work?
CKYC operates through a collaborative effort between individuals, KYC Registration Agencies (KRAs), financial institutions, and CERSAI. Here's a breakdown of the process:
For Individuals-
1. CKYC Registration
Individuals initiate the CKYC process by approaching a KRA or a participating financial institution. The KRA or institution collects the required KYC documents (PAN card, address proof, etc.) and begins the verification process. This can be an in-person verification or eKYC (electronic KYC), depending on the available option.
2. CERSAI Verification:
Once the KYC documents are submitted, CERSAI performs a thorough verification, ensuring the authenticity and accuracy of the information.
3. Unique CKYC Number:
After successful verification, CERSAI assigns a unique 14-digit CKYC identification number to the individual. This number serves as a single point of reference for all future KYC needs across participating financial institutions.
For Businesses-
1. Customer Shares CKYC Number:
During customer onboarding, a business can inquire if the customer has a CKYC number.
2. CKYC Information Retrieval:
If the customer possesses a CKYC number, the business can retrieve their KYC details directly from the CERSAI database with the customer's consent. This retrieval process typically happens electronically through APIs offered by CERSAI or authorized service providers.
3. Seamless Verification:
Once the KYC details are retrieved, the business can verify the customer's information and proceed with account opening or product offering without the need for further document collection or verification.
Key Points to Remember:
- Individuals only need to undergo CKYC once. Their KYC information remains valid for a specific period (typically 10 years) unless there are any changes requiring an update.
- Businesses and financial institutions can leverage CKYC APIs to seamlessly integrate KYC verification into their existing workflows, further streamlining the customer onboarding process.
Read more- The intricacies of CKYC operations
What is the process of KYC registration?
The CKYC process involves two key stages: registration and verification. Let's delve deeper into each stage to understand the steps involved for both individuals and businesses or financial institutions.
CKYC Registration Process
- Initiating the Process:
As mentioned earlier, individuals can initiate CKYC registration by approaching either a KYC Registration Agency (KRA) or a participating financial institution. KRAs are entities authorized by CERSAI to facilitate KYC registration.
- Required Documents:
During registration, individuals need to submit a set of documents as mandated by CERSAI. These typically include:
- Proof of identity (PAN card, Aadhaar card, etc.)
- Proof of address (utility bills, voter ID card, etc.)
- Photograph
- Signature
- Verification Methods:
The verification process can be conducted in two ways-
1. In-person Verification (IPV)
A KRA or financial institution representative physically verifies the individual's documents and identity.
2. eKYC Verification
This paperless approach leverages electronic document verification and biometric authentication for faster processing. However, the availability of eKYC may vary depending on the KRA or institution.
Steps Involved in CKYC Verification
Step 1- Document Scrutiny
Upon receiving the KYC documents, CERSAI meticulously examines them for authenticity and accuracy. This may involve data validation checks with issuing authorities.
Step 2- Information Verification
CERSAI might also verify the information provided against other databases to ensure its correctness.
Step 3- Discrepancy Resolution
If any discrepancies are found during verification, CERSAI will notify the individual and the KRA or institution involved for further action and potential re-submission of documents.
Step 4- Successful Verification:
Once all checks are cleared, CERSAI assigns a unique 14-digit CKYC number to the individual, signifying successful registration.
Types of Central KYC Accounts
The CKYC system sorts accounts based on the type of documents used for verification. While the core benefits of a single KYC identifier remain the same, these categories offer insights into the verification methods used. Here are the different types of CKYC accounts:
1. Normal Account:
This is the most common type of CKYC account. It's created when a person submits any of the following six officially valid documents (OVDs) as proof of identity:
- PAN Card
- Aadhaar Card (Preferred due to electronic verification capabilities)
- Voter ID Card
- Passport
- Driving License
- NREGA Job Card (National Rural Employment Guarantee Act)
2. Simplified Measures Account:
This account comes into play when a person submits Officially Valid Documents (OVDs) other than the six listed for the Normal Account. The CKYC identifier for Simplified Measures Accounts will be prefixed with an "L" to distinguish them from Normal Accounts.
3. Small Account:
This is the most basic type of CKYC account. It allows individuals to open single accounts with multiple financial institutions without going through a full KYC process. However, there are limitations on transaction value or types of financial products accessible.
Small accounts are created when a person submits only their personal details and a photograph. An “S” is prefixed as the KYC identifier for small accounts.
4. OTP-based eKYC Account:
This account leverages Aadhaar for verification. Here, customer identification and document submission are bypassed in favour of an Aadhaar-based electronic KYC (eKYC) process.
When a person provides their Aadhaar number, the financial institution initiates an OTP (One-Time Password) verification directly with UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India). Upon successful verification, an OTP-based eKYC account gets created with a CKYC identifier prefixed with an "O."
What is the Difference Between KYC, eKYC & CKYC?
While the purpose is always grounded in avoiding financial fraud, their functionalities differ significantly:
KYC (Know Your Customer):
KYC is the overarching term encompassing all customer identification and verification procedures employed by financial institutions.
It refers to the general regulations that require institutions to gather and verify customer information to combat money laundering and fraud. KYC can involve various methods, including document verification, background checks, and risk assessments.
eKYC (electronic KYC):
eKYC is a paperless alternative to the traditional method of KYC verification by leveraging online document verification and biometric authentication (fingerprint scans or facial recognition) to confirm an individual's identity electronically. Customers can submit documents online or undergo Aadhaar-based OTP authentication, eliminating the need for physical documents.
CKYC (Central KYC):
CKYC is a centralized repository for customer KYC information. It acts as a secure database where verified KYC details are stored after a customer completes the KYC process with a participating financial institution.
CKYC eliminates the need for repeated KYC procedures across different institutions. A customer simply provides their unique CKYC number for verification, saving time and effort.
Here's an analogy to simplify the concept:
Imagine a library. KYC represents the overall library system with various verification methods like borrowing cards and ID checks. eKYC is like an online library card application, allowing for digital verification. Finally, CKYC is a central database that stores your library member information, eliminating the need to re-register at every branch you visit.
KYC vs eKYC vs CKYC:
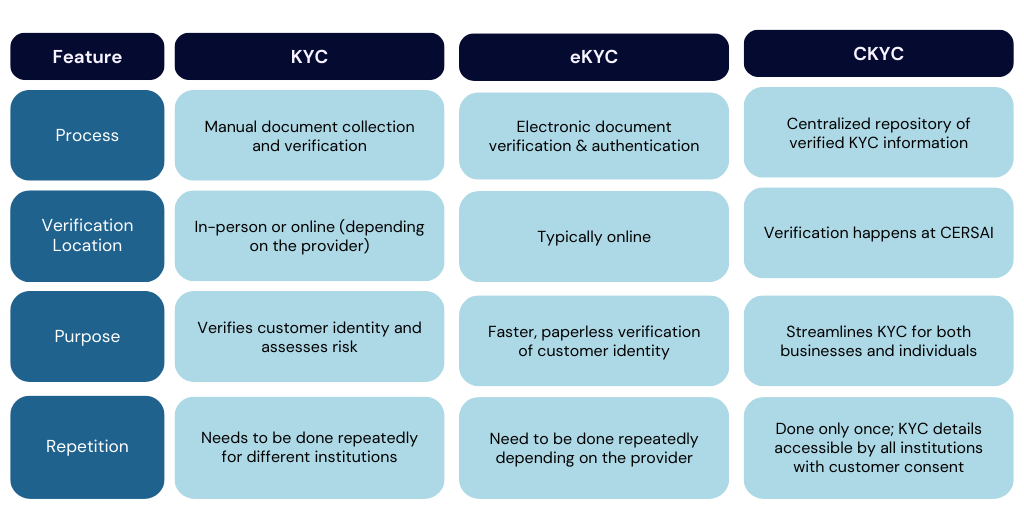
In simpler terms, KYC is the foundation, eKYC offers a faster way to build upon that foundation, and CKYC creates a centralized structure to store and share verified KYC information efficiently.
Why CKYC is Important?
CKYC holds immense significance for the entire financial ecosystem in India. Here's why widespread CKYC implementation is crucial:
- Combating Financial Fraud:
In 2023, around 1.1 million financial fraud cases were registered in India. Traditional KYC processes with potential loopholes can be exploited by fraudsters. CKYC, with its centralized verification and standardized procedures, strengthens safeguards against identity theft and fraudulent account openings.
- Improved Financial Inclusion:
CKYC simplifies KYC procedures, making it easier for individuals, particularly those residing in remote areas or with limited documentation, to access formal financial services. A study by the World Bank suggests that financial inclusion can contribute to a higher percentage point increase in GDP per capita growth in developing countries.
- Enhanced Transparency:
CKYC fosters greater transparency within the financial sector. The centralized KYC repository provides a clear audit trail for customer information, making it easier for authorities to track suspicious activities and deter financial crimes.
Why CKYC is Essential for Financial Institutions
While CKYC benefits the entire financial ecosystem, financial institutions too stand to gain significant advantages:
- Faster Customer Onboarding:
No more repetitive document collection and verification! CKYC allows you to onboard new customers swiftly using verified information from the CERSAI repository.
- Reduced Operational Costs:
CKYC eliminates the need for in-house document storage, manual verification processes, and related manpower requirements. These cost savings can be reinvested into core business activities or customer-centric initiatives.
- Enhanced Efficiency:
Streamlined KYC procedures free up valuable resources within your organization. Your team can focus on core competencies like product development, customer relationship management, and risk assessment.
- Improved Risk Management:
CKYC ensures a higher level of data accuracy and standardization within the KYC process. Centralized verification procedures minimize discrepancies that can lead to misinformed risk assessments.
- Compliance with Regulations:
CKYC adheres to the latest KYC guidelines set forth by the RBI and other financial regulatory bodies. By leveraging CKYC, you can ensure compliance with KYC regulations and mitigate potential risks associated with non-compliance.
Challenges of the CKYC Process for Businesses and Financial Institutions
While CKYC promises a smoother and more efficient KYC landscape, integrating it into existing business operations isn't without its challenges:
- Integration Challenges:
Seamlessly integrating CKYC with existing KYC workflows and IT infrastructure can be a complex task. Financial institutions might need to adapt or upgrade their internal systems to ensure smooth data exchange with the CERSAI repository.
- Process Changes and Training:
Implementing CKYC necessitates adjustments to existing customer onboarding procedures. Businesses need to train their staff on the new CKYC protocols, including the CERSAI platform, understanding data retrieval processes, and ensuring customer consent for KYC information sharing.
- Data Discrepancies:
Even with CKYC's centralized verification procedures, there's a possibility of data discrepancies arising between information submitted during CKYC registration and the details available with the issuing authorities.
Fortunately, solutions are available to streamline the process and maximize the benefits of CKYC.
How Arya’s KYC Can Help Simplify the Central KYC for Your Business
1. Effortless CERSAI Integration:
Our CKYC API handles the complexities of data exchange, ensuring flawless communication between your existing systems and the central KYC database. Your team doesn’t have to invest time and resources in developing or maintaining custom integrations.
2. Simplified Data Management:
Arya AI's CKYC module meticulously parses through the data retrieved from CERSAI. We filter and categorize the retrieved information, showing only the essential details relevant to your KYC processes in a clear and concise format.
3. Automated Document Tagging:
Our solution automatically classifies and tags all retrieved documents, such as photos, signatures, PAN cards, or Aadhaar copies. This eliminates manual document sorting and categorization tasks, saving your team valuable time and minimizing the risk of human error.
4. Advanced Efficiency:
By streamlining CKYC data retrieval, parsing, and document management, Arya AI CKYC significantly improves the efficiency of your customer onboarding processes. This means faster onboarding times, reduced administrative burdens, and improved customer satisfaction.
5. Data Discrepancy Mitigation:
Arya AI's CKYC solution can flag potential inconsistencies and alert your team for further investigation, helping to ensure data accuracy and prevent delays in customer onboarding.
Additionally, Arya AI offers a comprehensive suite of KYC APIs that can further enhance your customer onboarding experience:
- KYC Extraction: For customers whose KYC details are not found in CERSAI, our KYC Extraction API can extract critical information directly from uploaded documents.
- Face Verification: The Face Verification API allows you to verify the identity of your customer by comparing a photo retrieved from CKYC with another photo ID, adding an extra layer of security to your onboarding process.
- Aadhaar Masking: Our Aadhaar Mask API adheres to UIDAI regulations by automatically masking the first eight digits of Aadhaar numbers retrieved from CKYC, ensuring customer privacy.
Empower your business with easy CKYC integration – schedule a call with us and we’ll help your business streamline KYC, reduce costs, and accelerate growth!